Exploring the Promising Path of a Career in Open Science
Exploring the Promising Path of a Career in Open Science https://opusproject.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/can-you-really-plan-your-career.webp 640 480 Open and Universal Science (OPUS) Project https://opusproject.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/can-you-really-plan-your-career.webpIn recent years, open science has emerged as a powerful movement transforming the traditional landscape of scientific research and discovery. By promoting transparency, collaboration, and accessibility, open science has the potential to accelerate scientific progress and foster innovation. As this approach gains traction, it opens up exciting opportunities for individuals seeking a fulfilling and impactful career. In this article, we delve into the realm of open science and explore the benefits and challenges associated with pursuing a career in this dynamic field.
Defining Open Science
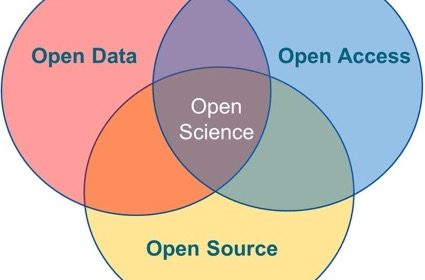
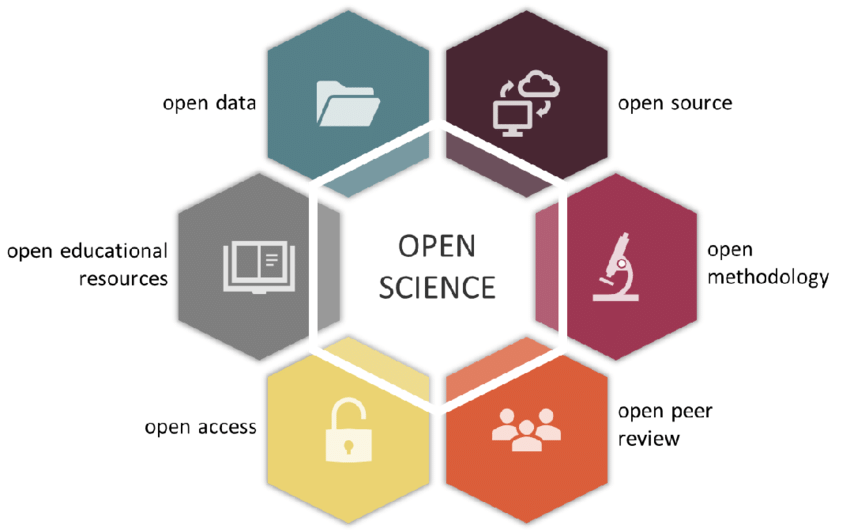
Open science is a philosophy and practice that aims to make scientific research, data, and findings accessible to everyone, without barriers such as paywalls or restrictive licenses. It encompasses various principles, including open access publishing, open data, open-source software, and open collaboration. Open science encourages researchers to share their work openly, facilitating transparency, reproducibility, and collaboration.
Benefits of a Career in Open Science
- Advancing knowledge and societal impact: Engaging in open science allows researchers to contribute to the collective body of knowledge and have a tangible impact on society. By making research findings accessible to a wider audience, open science promotes scientific literacy and enables policymakers, industry professionals, and the public to make informed decisions based on evidence.
- Collaboration and networking: Open science emphasizes collaboration and encourages researchers to work together across disciplines, institutions, and borders. This fosters a rich and diverse scientific community, enabling the exchange of ideas, expertise, and resources. Collaborative efforts often lead to more robust and comprehensive research outcomes.
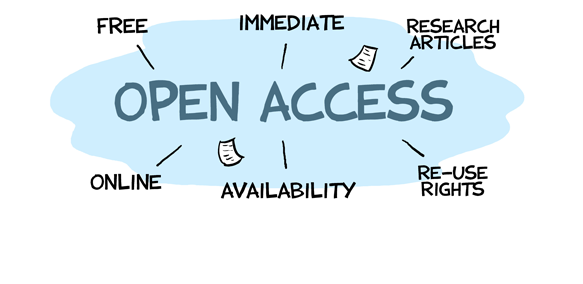
- Career development and visibility: Open science provides researchers with increased visibility and recognition within their fields. Publishing in open access journals or sharing preprints allows rapid dissemination of their work, potentially attracting collaborations and future opportunities. Additionally, contributing to open-source software projects or participating in open data initiatives can enhance technical skills and broaden professional networks.
- Reproducibility and quality assurance: Open science promotes transparency and reproducibility, ensuring that research findings can be verified and validated by others. Engaging in open practices, such as sharing raw data and methodologies, enhances the quality and integrity of scientific research. This commitment to rigor and transparency strengthens the credibility of researchers and their work.
Challenges and Considerations
While the pursuit of a career in open science offers numerous advantages, it is important to acknowledge the challenges and considerations involved:
- Funding and sustainability: Open science initiatives often rely on alternative funding models. Researchers may need to secure grants, crowdfund, or seek support from institutions committed to open science. Additionally, sustainability of open science practices can pose challenges, as infrastructure and maintenance costs may need to be covered in novel ways.
- Cultural shift and resistance: Shifting towards open science requires a cultural change within the scientific community. Researchers may encounter resistance from traditional establishments, who might be reluctant to embrace open practices. However, as open science gains momentum, attitudes are gradually evolving, making it an opportune time to contribute to this transformative movement.
- Balancing openness and privacy: While open science promotes sharing and collaboration, it is crucial to navigate privacy and ethical considerations associated with sensitive data, human subjects, and intellectual property. Striking a balance between openness and safeguarding privacy rights is an ongoing challenge that requires careful consideration.
Conclusion
A career in open science holds immense potential for individuals passionate about driving scientific progress, fostering collaboration, and making a positive impact on society. Embracing open practices allows researchers to accelerate their own career development, while contributing to a more inclusive and accessible scientific ecosystem. Despite the challenges involved, the rewards of open science are substantial, both in terms of personal fulfillment and the advancement of knowledge for the benefit of all. By championing transparency, collaboration, and open access, those embarking on a career