Open Access Faculty Toolkit
Open Access Faculty Toolkit https://opusproject.eu/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/2024-07-15_11h06_35.png 994 765 Open and Universal Science (OPUS) Project https://opusproject.eu/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/2024-07-15_11h06_35.pngIntroduction
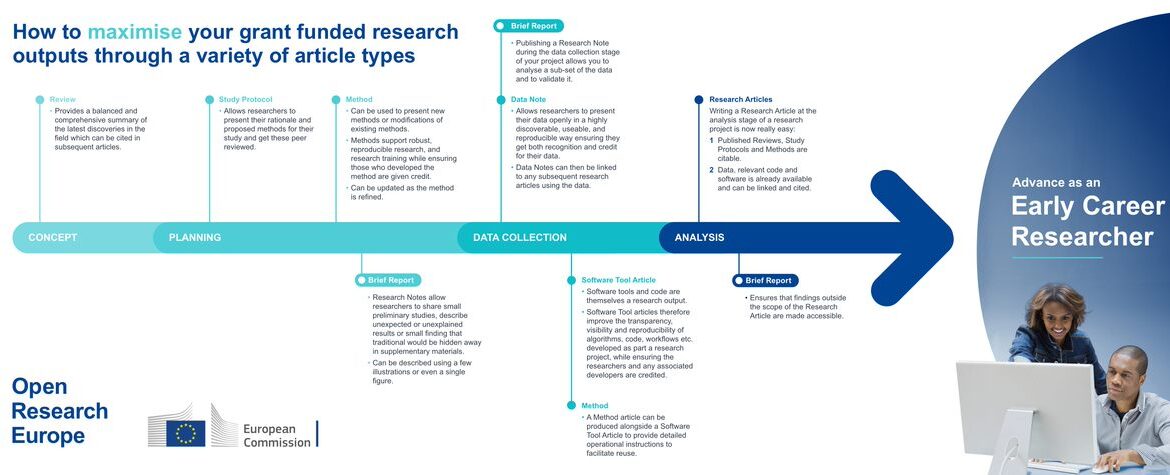
This toolkit is designed to assist faculties at Utrecht University in implementing and developing their own multi-channel publication strategies from 2024 onwards. Aligned with Utrecht University’s open access strategy and tailored to faculty and departmental priorities and budgets, the toolkit compiles the publication knowledge of the Publishing Support Department at Utrecht University Library. Multiple pathways to open access publishing coexist, each with distinct characteristics and merits related to visibility, uptake, recognition in the field, funder compliance, and cost. This document aims to provide guidance on preferred and supported publication routes based on specific faculty needs.
Books
Diamond Open Access
Pros:
- No open access fees for authors.
- Broad visibility and equitable access.
- Suitable for books with a built-in audience, such as textbooks and conference proceedings.
Cons:
- May lack the prestige of traditional publishers, particularly for early career researchers.
- Limited access to reputable diamond publishers in some fields.
Faculty Checklist:
- Discuss diamond options and promote them among researchers.
- Consider financially supporting diamond publishers.
- Decide on policies regarding optional Book Publishing Charges (BPCs).
University Library Support Services:
- Provide overviews of existing diamond publishers.
- Offer direct financial support to diamond infrastructures.
- Support the Open Book Collective, which aids diamond OA publishers.
Self-Publishing
Pros:
- No open access fees.
- Cost-effective for students and libraries.
- Excellent for regularly updated books and mixed media content.
Cons:
- Perceived lack of prestige.
- Authors handle peer review, editing, and formatting themselves.
Faculty Checklist:
- Recognize and reward the development of open textbooks.
- Encourage the use of open textbooks in courses.
- Consider financial support for editing and peer review services.
University Library Support Services:
- Pilot subscription to Pressbooks for self-publishing open textbooks.
- Offer courses on developing open textbooks through GitHub.
Green Open Access
Pros:
- No costs involved.
- Minimal author workload with the Taverne workflow.
Cons:
- Limited application for entire books.
- 6-month embargo period under the Taverne route.
- Authors must initiate registration and upload for some works.
Faculty Checklist:
- Evaluate the adequacy of Taverne for book chapters.
- Consider options for immediate OA for book chapters.
University Library Support Services:
- Manage repository and Taverne-related workflows.
- Assist authors with license negotiations and self-archiving options.
- Keep faculties informed on Rights Retention Strategy (RRS) developments.
Articles
Preprints and Preprint Servers
Pros:
- Fast and open access to research.
- Early visibility and feedback.
- Acceptable for grant applications with some funding organizations.
Cons:
- Variable quality checks on preprint servers.
- Do not replace full OA publications.
- Some publishers do not accept preprints.
Faculty Checklist:
- Develop a preprint publishing strategy.
- Identify trusted preprint servers in relevant fields.
- Inform authors about preprint policies of selected journals.
University Library Support Services:
- Financial support for preprint infrastructures.
- Educate on preprint workflows and journal-independent peer review.
- Advise on preprint servers and quality checks.
Diamond Open Access
Pros:
- No publishing fees for authors or readers.
- Equitable and cost-effective.
- Supported by national and international organizations.
Cons:
- Emerging field with potential scalability issues.
- May lack indexing in restrictive search engines like WoS/Scopus.
Faculty Checklist:
- Promote diamond options and encourage support for diamond journals.
- Consider converting APC-based journals to diamond.
University Library Support Services:
- Provide overviews of diamond journals and platforms.
- Support the transition to and funding of diamond journals.
Gold Open Access Based on Article Processing Charges (APC)
Pros:
- Financial sustainability for journals.
- Lower average costs for UU researchers compared to hybrid journals.
- Greater audience reach and visibility for authors.
Cons:
- Financial barriers for authors without funds.
- Additional workload for securing funding and handling invoices.
- Potential quality assurance issues and predatory journals.
Faculty Checklist:
- Establish criteria for APC funding and budget allocation.
University Library Support Services:
- Manage OA agreements and inform researchers on funding options.
- Assist faculties in budget allocation for open access publishing.
Hybrid Open Access
Pros:
- Access to established journals.
- Administratively easy for authors due to existing deals.
Cons:
- Temporary nature of APC waivers.
- Continued perpetuation of unequal access to information.
- Non-compliance with some funding agencies’ OA requirements.
- Deals favor disciplines with higher publishing output.
Faculty Checklist:
- Evaluate the desirability of supporting hybrid OA.
- Consider faculty-level deals with smaller publishers.
University Library Support Services:
- Manage OA agreements and report on trends in research output.
Final Considerations
The Open Access Faculty Toolkit is a comprehensive guide to help faculties at Utrecht University navigate the complex landscape of open access publishing. It provides detailed information on various open access routes for books and articles, along with practical checklists and support services from the University Library. As the open access landscape evolves, the toolkit will be regularly updated to reflect new developments and maintain its relevance.
de Boer, J., Bosman, J., Holwerda, F., Jetten, N., Livio, C., Ryane, N., Shetty, R., de Vries, H., & Utrecht University Library – Publishing Support. (2024). Open Access Faculty Toolkit. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.12703515